|
Real-Time Eye Gaze Tracking Under Natural Head Movements
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
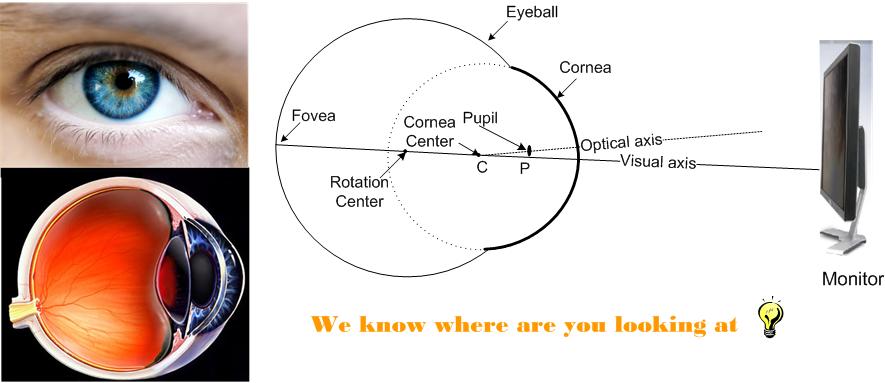
Eye gaze is defined as the line of sight of a
person. It represents a person's focus of attention. Eye gaze tracking has
been an active research topic for many decades because of its potential
usages in various applications such as Human Computer Interaction (HCI),
Virtual Reality, Eye Disease Diagnosis and Human Behavior Study, etc.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Unlike most of the existing gaze tracking
techniques, which often require a static head to work well and require a
cumbersome calibration process for each person, our gaze tracker can
perform robust and accurate gaze estimation under natural head movements
with only one-time calibration. We have developed three
different gaze tracking systems based on different configurations:
Our proposed methods will dramatically increase the
usability of the eye gaze tracking technology, and we believe that it is a
big step for the eye tracker to be accepted as a natural computer input
devices.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Stereo-Camera Eye Gaze Tracker
|
|
|
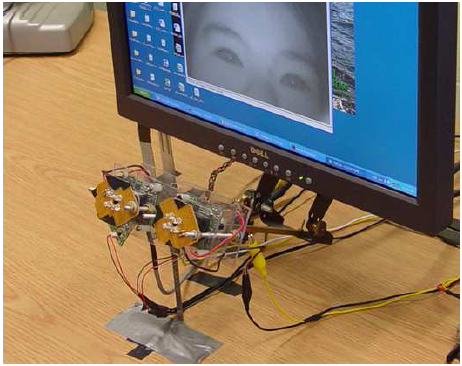
In this system, the 3D eye position can be
obtained by a pair of stereo cameras. Then, we have two algorithms to
accommodate the eye position changes : (A) Based on the obtained eyeball
position, the gaze mapping function at the new position can be automatically
updated by the proposed dynamic computational head compensation model to
accommodate the eye position changes. (B) By the proposed 3D gaze tracking,
we can directly estimate the 3D virtual axis without any mapping functions.
Both of the two proposed method can achieve the accracy less than 1 degree.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fig.1
Configuration of stereo camera system
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Publications:
|
|
|
(1) Zhiwei Zhu and Qiang Ji, " Novel Eye Gaze
Tracking Techniques Under Natural Head Movement," to appear in
IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering.
(2) Zhiwei Zhu, Qiang Ji, "Eye Gaze Tracking
Under Natural Head Movements." International Conference on
Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR05), San Diego, CA, June 2005.
(3) Zhiwei Zhu, Qiang Ji, "Eye Gaze Tracking
Under Natural Head Movements." International Conference on
Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR05), San Diego, CA, June 2005.
(4) Zhiwei Zhu, Qiang Ji, "Eye and Gaze
Tracking for Interactive Graphic Display." Machine Vision and
Applications, Pages 139-148, Vol.15, No.3, July 2004.
(5) Qiang Ji, Zhiwei Zhu, "Eye and Gaze
Tracking for Interactive Graphic Display." 2nd International
Symposium on Smart Graphics, Hawthorne, NY, USA, June 11-13, 2002.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Demos:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|

|
|
|
Eye gaze tracking demo
|
Map control via eye gaze
|
Word reading via eye gaze
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note: in the first demo, the static cirles with different
colors represent the reference objects that the user will look at. The
blinking square that changes locations is the estimated gaze point,
representing where the user is looking at.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
back
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Multi-Camera Eye Gaze Tracker
|
|
|
This system is based on one-camera gaze
estimation algorithm. By this algorithm, the 3D eyeball position can be
estimated by the two corneal reflections (glints) of the IR lights. In our
multi-camera gaze tracker, each camera can estimate the gaze independently,
So it allows very large head movement. The accuracy of this system is also
less than 1 degree.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Fig.2
One-camera gaze estimation algorithm
|
Fig.3 Captured image by one
camera
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
Fig.4 Configuration of two
camera system. (Note: each of the two camera can track the eye
independently. So the allowed head movement is very large)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
back
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Eye Gaze Tracking With a Monocular Camera
and a Steering Mirror
|
|
|
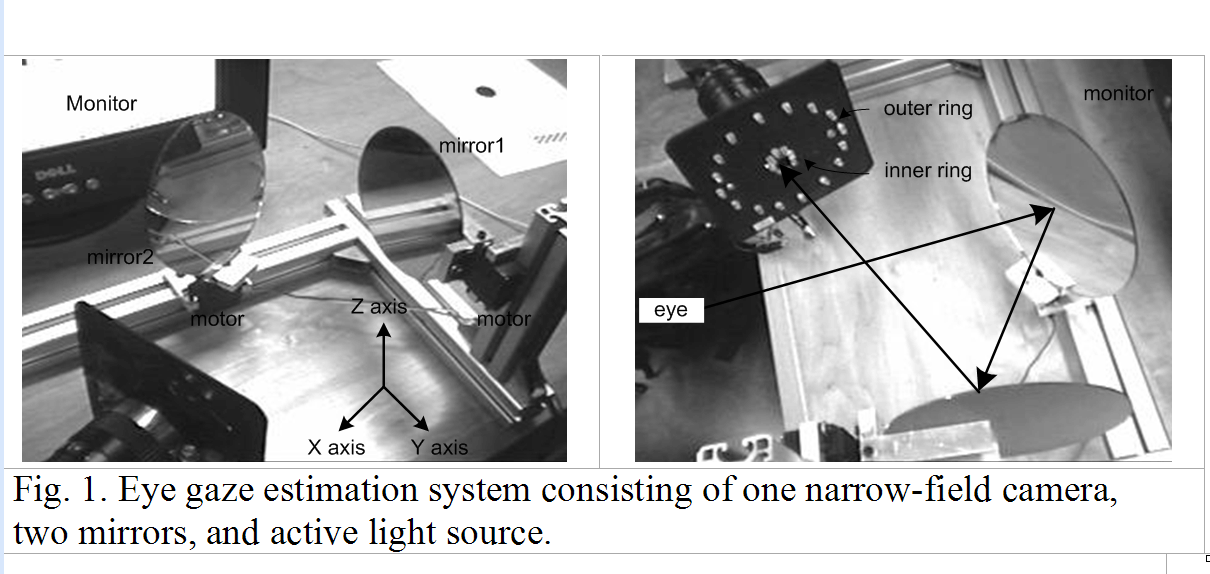
We propose an eye gaze tracking system under
natural head movements. The system consists of one CCD camera and two
mirrors. Based on geometric and linear algebra calculations, the mirrors
rotate to follow head movements in order to keep the eyes within the view
of the camera. Our system allows the subjects head to move 30 cm
horizontally and 20 cm vertically, with spatial gaze resolutions about 6
degree and 7 degree, respectively and a frame rate about 10 Hz. We also
introduce a hierarchical generalized regression neural networks (H-GRNN)
scheme to map eye and mirror parameters to gaze, achieving a gaze
estimation accuracy of 92% under head movements. The use of H-GRNN also
eliminates the need for personal calibration for new subjects since H-GRNN
can generalize. Preliminary experiments show our system is accurate and
robust in gaze tracking under large head movements. For details, see
publication 4 above.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Publications:
|
|
|
(1) Soochan Kim and Q. Ji, Non-intrusive Eye Gaze Tracking
Under Natural Head Movements, 26th Annual International Conference IEEE
Engineering in Medicine and Biology, Sep., 2004
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
back
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|